- Guides
- 6 likes
- 0 comments
- Direct or Alternating Current
Navigation index
- Difference between direct and alternating current
- Applications of direct and alternating current
- Advantages and disadvantages
Direct current (DC) and Alternating current (AC) are two different ways of supplying electricity. Both forms of electricity are widely used in electrical devices, but there are important differences between them. In this article we will look at the main differences between direct current and alternating current and the applications of both forms of electricity.
Difference between direct and alternating current
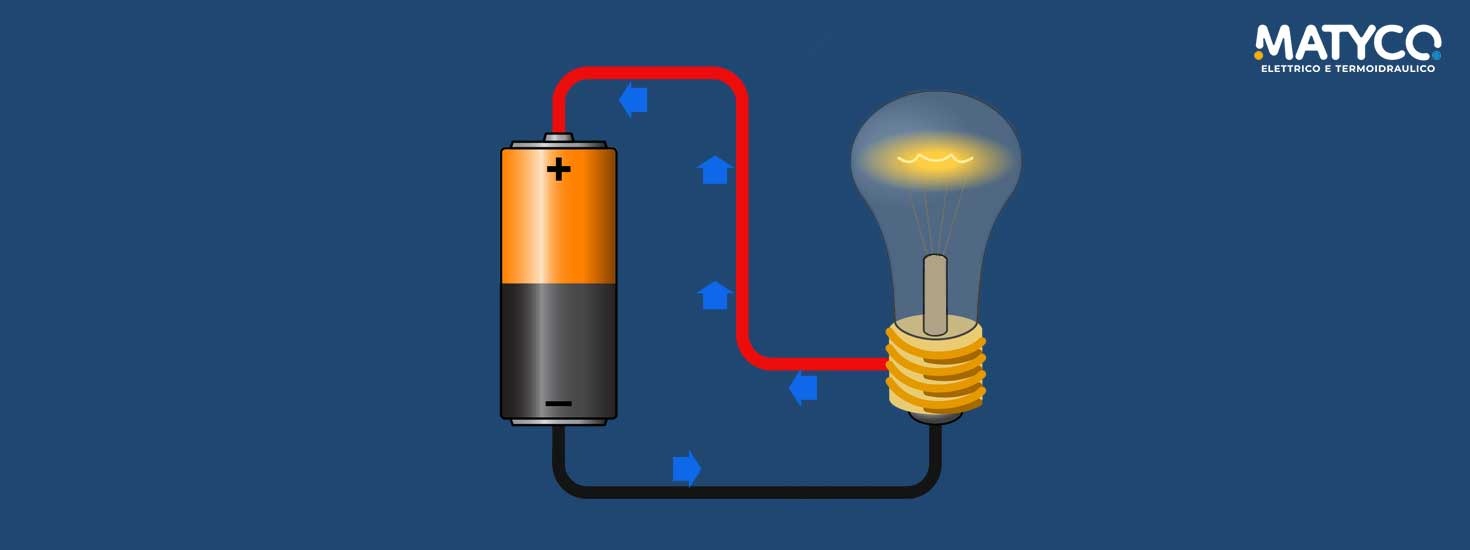
The main difference between direct current and alternating current is the direction of current flow. Direct current has a constant direction, while alternating current changes direction at regular intervals. Direct current is produced by batteries, while alternating current is produced by generators.
Another difference between direct current and alternating current is their voltage. Direct current is usually low voltage, while alternating current is higher voltage. To convert alternating current into direct current, a device called a current converter is required.
Applications of direct and alternating current
Direct current is widely used in batteries, transformers, and electronic devices such as computers, cell phones, and televisions. Alternating current is often used to supply energy for homes and commercial buildings. It is also used in some electronic devices, such as air conditioners, which may require a higher voltage.
Advantages and disadvantages
Direct current has an advantage in terms of energy efficiency, as there is no loss of energy during the conversion from one form to another. Alternating current, on the other hand, has a cost advantage, since it does not require the use of current conversion devices. A disadvantage of alternating current is that it can cause electromagnetic interference in some electronic devices.
Direct current and alternating current are both important forms of electrical energy. Despite their differences, they are both used in everyday electronic devices. Choosing the right form of electricity depends on the specific needs of the device.

Comments (0)